타입스크립트 타입 종류 살펴보기
The primitives
- string
- number
- boolean
// 변수 타입 표기 - 변수의 타입을 지정한다.
const num: number = 1;
const str: string = '문자열';
const bool: boolean = true;
// 타입 추론 : 'name' 변수는 'string' 타입으로 추론된다.
const name = '최개발';
any
TypeScript가 주는 장점을 모두 상쇄시켜 JavaScript를 사용하는 것과 같게 된다. any타입을 사용하는 곳에서는 TypeScript 컴파일러가 작동하지 않는다. 아래의 경우를 제외하고는 any타입을 사용하지 않는 것이 좋다.
- 특정 값으로 인하여 타입 검사 오류가 발생하는 것을 원하지 않는 경우
- 어떤 값 혹은 데이터가 저장될지 알 수 없는 경우
any타입은 tsconfig.json에 설정된 noImplicitAny 설정 값이 true인 경우 암묵적으로 any로 간주되는 모든 경우 에러를 발생시킨다.
let anyType: any;
// any타입은 어느 값을 할당하여도 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
anyType = 1;
anyType = '가';
anyType = true;
unknown
사용자가 어떤 값을 입력할지 모르는 경우 사용한다.
let unknownUserInput: unknwon;
let userName: string;
// any와 비슷하게 어떤 타입이든 에러 없이 저장이 가능하다.
unknownUserInput = 1;
unknownUserInput = '가';
// string 타입의 변수에 unknown 타입 값을 할당하면 에러가 발생한다.
userName = unknownUserInput; // Type 'unknown' is not assignable to type 'string'.
// string 타입의 변수에 any 타입 값을 할당하면 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
let anyUserInput: any = 1;
userName = anyUserInput; // any는 타입확인을 수행하지 않음
// unknown을 다른 변수에 할당하고 싶을 때는 타입 검사를 진행하면 된다.
if (typeof unknownUserInput === 'string') userName = unknownUserInput;
Arrays
// number[] - number 타입만 허용
const nums: number[] = [1, 2, 3];
// string[] - string 타입만 허용
const strs: string[] = ['가', '나', '다'];
// boolean[] - boolean 타입만 허용
const bools: boolean[] = [true, false];
// any[] - 모든 타입 허용
const anys: any[] = [1, '가', true];
// 명시한 특정 타입 허용
const specific: (number | string)[] = [1, '가'];
Tuple
아이템 순서를 지정하고, 각 아이템은 지정된 타입만 허용된다.
// 올바른 방법
let person: [string, number] = ['최개발', 28];
// Tuple과 일치하지 않는 요소가 들어간 경우 아래와 같은 에러가 발생한다.
// Type '[string, number, boolean]' is not assignable to type '[string, number]'.
// Source has 3 element(s) but target allows only 2.
person: [string, number] = ['최개발', 28, true];
// Tuple과 일치하면 재할당도 가능하다.
person = ['김개발', 24]; // OK
person = [26, '이개발']; // ERROR
// Tuple은 push를 예외적으로 허용되기에 에러가 발생하지 않는다.
person.push('김개발'); // ['최개발', 28, '김개발']
// push를 예외적으로 허용하지만 허용한 타입이 아닌 경우 아래와 같은 에러가 발생한다.
// Argument of type 'boolean' is not assignable to parameter of type 'string | number'.
person.push(true);
Functions
TypeScript는 함수 입력 및 출력 타입을 지정할 수 있다. 익명 함수의 경우 함수가 어떻게 호출되는지 알아내고 매개 변수에 자동으로 타입을 부여하는 특징이 있다.
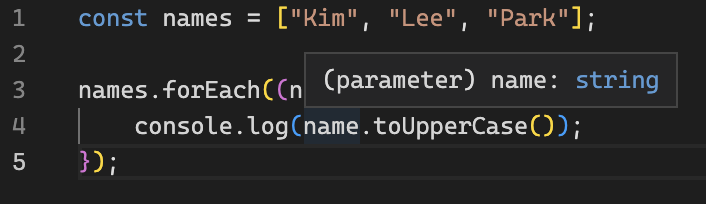
// 1. 매개변수 타입 표기
const greet = (name: string) => {
console.log('Hello, ' + name);
};
// 2. 반환 타입 표기
const getNumber = (): number => {
return 28;
};
// 3. Function 타입 표기
const add = (num1: number, num2: number) => {
return num1 + num2;
};
let combineValues: Function;
combineValues = add;
// 어떤 타입의 매개변수를 받고, 어떤 타입의 값을 반환할지 명확하게 설정할 수 있다.
let addValues: (a: number, b: number) => number;
// callback 함수 만들어보기
const addHandle = (num1: number, num2: number, cb: (num: number) => void) => {
const result = num1 + num2;
cb(result);
};
addHandle(1, 2, (result) => {
console.log(result);
}); // 3
void
값을 반환하지 않는 함수의 반환 값을 의미한다. return문이 없거나 명시적으로 값을 반환하지 않았을 때 추론되는 타입이다.
// 타입 추론된 반환 값은 void이다.
const noop = () => {
return;
};
Object Types
객체 타입은 프로퍼티와 각 프로퍼티 타입을 나열하면 된다. 각 프로퍼티 타입 표기는 선택 사항이며 타입을 지정하지 않을 경우 any타입으로 간주한다.
const person: {
name: string;
age: number;
hobbies: string[];
} = {
name: '최개발',
age: 28,
hobbies: ['Coding', 'Camping'],
};
Union Types
서로 다른 두 개 이상의 타입을 |로 구분하여 타입을 지정하며, 각 타입을 멤버라고 부른다. Union 타입은 모든 멤버의 타입을 허용한다.
let id: string | number;
id = 123;
id = '가나다';
id = true; // ERROR
Union 타입에 메서드를 사용하기 위해서는 모든 멤버에 유효한 작업이어야 한다.
const printUpper = (str: string | string[]) => {
console.log(str.toUpperCase());
// Property 'toUpperCase' does not exist on type 'string | string[]'.
};
// 위 문제는 타입 검사를 통해 해결이 가능하다.
const printUpper = (strs: string | string[]) => {
if (typeof strs === 'string') {
console.log(strs.toUpperCase());
} else {
strs.forEach((str) => {
console.log(str.toUpperCase());
});
}
};
Type Aliases
같은 타입을 재사용하거나 이름을 붙이고 싶을 때 사용한다.
// Object 타입 별칭. 이외에도 Primitive, Union 등 모든 타입을 저장할 수 있다.
type Person = {
name: string;
age: number;
};
const greet = (person: Person) => {
console.log(person.name + ' is ' + person.age + ' years old');
};
greet({ name: '최개발', age: 28 }); // "최개발 is 28 years old"
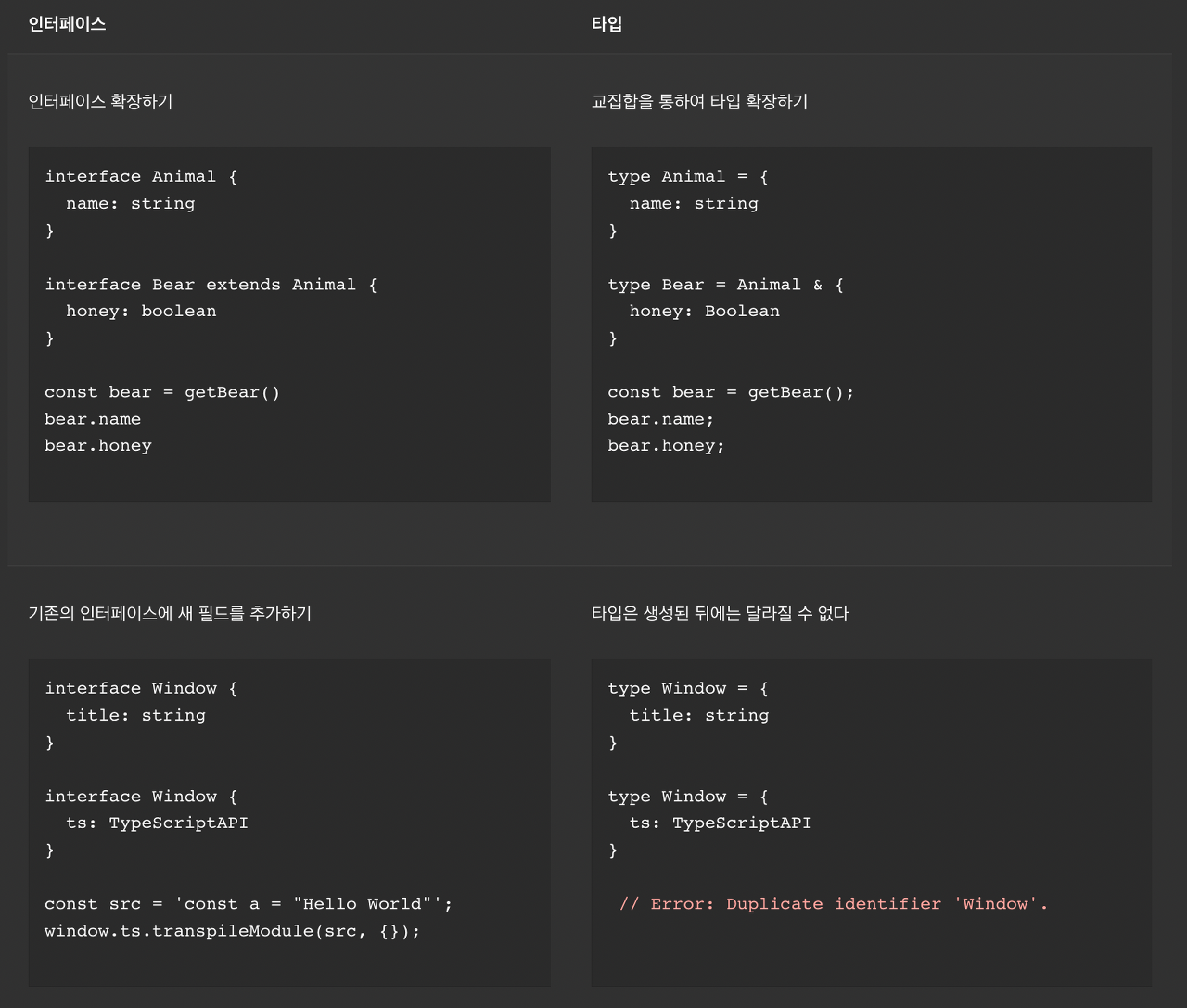
Interfaces
Interface의 대부분 기능은 type alias에서도 가능하며 이름을 부여해준다는 점이 동일하다.
interface Person {
name: string;
age: number;
}
const printPerson = (person: Person) => {
console.log(person.name);
console.log(person.age);
};
printPerson({ name: '최개발', age: 28 });
Interface는 객체 타입에만 이름을 다는 것이 가능하지만, type alias는 모든 타입에 이름을 달 수 있다.
Type Assertions
TypeScript가 추론한 타입보다 본인이 타입에 대한 정보를 더 정확히 아는 경우 타입 단언을 통해 더 구체적으로 명시할 수 있다. 보다 구체적이거나 덜 구체적인 타입으로 변환하는 것만 허용되며, 숫자형을 문자형으로 단언하는 것은 불가능하다.
// TypeScript는 document.getElementById는 HTMLElement 중 무언가 반환된다는 것만 알고있다.
// const myCanvas: HTMLElement | null로 타입 추론
const myCanvas = document.getElementById('main_canvas');
// type assertion
const myCanvas2 = document.getElementById('main_canvas') as HTMLCanvasElement;
// type assertion2
const myCanvas2 = <HTMLCanvasElement>document.getElementById('main_canvas');
Literal Types
구체적인 '값'을 가지는 타입이다. 예시로 boolean 타입은 실제로는 리터럴 타입으로 true | false의 type alias이다.
// const로 선언한 변수는 리터럴 타입으로 추론된다.
const num = 1; // const num: 1
// Literal Type으로 지정한 값만 허용된다.
const printName = (greet: string, userName: '최개발' | '김개발') => {
console.log(greet + userName);
};
printName('Hello, ', '최개발'); // Hello, 최개발
printName('Hello, ', '이개발'); // Argument of type '"이개발"' is not assignable to parameter of type '"최개발" | "김개발"'.
never
일반적으로 함수의 리턴 타입으로 사용되며, 리턴 타입으로 never를 사용하면 오류를 출력하고 리턴 값을 생성하지 않음을 의미한다.
const generateError = (message: string, code: number) => {
throw { message: message, errCode: code };
};
generateError('에러 발생', 500);
null, undefined
빈 값, 초기화되지 않은 값을 가리키는 원시 값이다.
const nullable: null = null;
const undefineable: undefined = undefined;
// null, undefined는 서로 다른 타입이다.
nullable = undefined; // ERROR
undefineable = null; // ERROR
tsconfig.json의 strictNullChecks 값에 따라서 동작 방식이 달라진다.
strictNullChecks: true
// 1. 모든 데이터 타입은 null 값을 할당할 수 없다.
let name: string = null; // ERROR! string 타입에 null 타입 할당
// null 값을 할당하기 위해서는 any, union 타입을 활용한다.
let name: string | null = null;
// 2. `null` 혹은 `undefined`의 값을 가졌을 때 해당 값을 테스트해야 한다.
const printName = (str: string | undefined) => {
if (str === undefined) {
...
} else {
...
}
};
strictNullChecks: false
// `null` 혹은 `undefined`의 값을 가져도 해당 값에 평소와 같이 접근할 수 있다.
// Null 검사의 부재는 버그의 주요 원인이 되며 해당 옵션을 설정하는 것을 권장한다.
let name: string = null;
Non-null Assertion 연산자
명시적인 검사를 하지 않고 null, undefined를 제거할 수 있는 구문으로 !연산자를 표현식 뒤에 붙여서 해당 값이 null, undefined가 아님을 단언한다.
const validate = (e?: Entity) => {
// 'e'는 null 혹은 유효한 값
};
const process = (e?: Entity) => {
validate(e);
const s = e!.name; // 'e'는 null이 아님을 단언하여 접근 가능하게 함.
};
Enums
멤버라고 불리는 명명된 값의 집합을 이루는 자료형이다. 숫자로 표현되지만 사람이 읽기 쉽도록 라벨링 하는 개념이며 해당 라벨들은 0부터 시작하는 숫자로 변환된다. 사용자 지정 타입이므로 첫 글자는 대문자로 입력하는 컨벤션을 지킨다.
// Numeric enums
enum Direction {
Up, // 0
Down, // 1
Left, // 2
Right, // 3
}
console.log(Direction.Up); // 0
// Numeric enums 값 할당 가능. 값이 할당되지 않은 멤버는 이전 멤버 +1된 값이 할당된다.
enum Direction {
Up = 10, // 10
Down, // 11
Left = 100, // 100
Right, // 101
}
console.log(Direction[101]); // "Right"
// String enums - 각 멤버는 문자열 리터럴 또는 다른 문자열 열거형 멤버로 상수 초기화 해야 한다.
enum Direction {
Up = 'UP',
Down = 'DOWN',
Left = 'LEFT',
Right = 'RIGHT',
}
Enums를 사용하는 이유
1. 역할을 부여하는 코드를 작성했다고 가정해본다.
// 0 : DEVELOPER
// 1 : ADMIN
// 2 : GUEST
const person = {
name: '최개발',
role: 0,
};
2. 해당 숫자 '0'만으로는 개발자, 관리자, 게스트 중 어떤 역할을 수행하고 있는지 이해하기 어려우며, 문자로된 식별자인 'DEVELOPER'가 더욱 이해하기 쉬울 것이다.
const person = {
name: '최개발',
role: 'DEVELOPER',
};
3. 다만 문자로된 식별자는 if문으로 권한을 확인할 때 'DEVELOPER'로 작성했는지 'developer'로 작성했는지 확신하기 어렵다. 문자열을 어떻게 작성했는지 정확하게 기억해야 한다는 단점이 있다.
if (person.role === 'DEVELOPER') {...} // O
if (person.role === 'developer') {...} // X
4. 3 번의 경우 보통 전역 상수를 선언하여 해결하곤 한다.
const DEVELOPER = 0;
const ADMIN = 1;
const GUEST = 2;
if (person.role === DEVELOPER) {...}
5. 전역 상수로 선언한 경우 role은 number 타입으로 추론되어 입력하지 않은 모든 숫자가 저장될 수 있다. 또한 전역 상수를 선언하여 상수들을 정의하고 관리해야 하는 어려움이 있다. 이러한 문제를 Enum을 통해 해결이 가능하다.
enum Role {
DEVELOPER, // 0
ADMIN, // 1
GUEST, // 2
}
const person = {
name: '최개발',
role: Role.DEVELOPER,
};
if (person.role === Role.DEVELOPER) {...}
Ref
'⭐️ Language > TypeScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 타입스크립트(TypeScript)란? (0) | 2022.08.18 |
|---|